Slovo ' Zkuste 'je úryvek ze slova' vyhledávání '. Trie je setříděná stromová datová struktura, která ukládá sadu řetězců. Má počet ukazatelů rovný počtu znaků abecedy v každém uzlu. Dokáže vyhledávat slovo ve slovníku pomocí předpony slova. Pokud například předpokládáme, že všechny řetězce jsou tvořeny písmeny ' A ' do' S ' v anglické abecedě může mít každý uzel trie maximálně 26 body.
jquery kliknutím
Trie je také známý jako digitální strom nebo strom předpon. Poloha uzlu v Trie určuje klíč, se kterým je tento uzel spojen.
Vlastnosti Trie pro množinu řetězce:
- Kořenový uzel trie vždy představuje nulový uzel.
- Každý potomek uzlů je řazen abecedně.
- Každý uzel může mít max 26 děti (A až Z).
- Každý uzel (kromě kořene) může uložit jedno písmeno abecedy.
Níže uvedený diagram znázorňuje ukázkové znázornění zvonu, medvěda, vývrtu, pálky, míčku, zastávky, pažby a zásobníku.
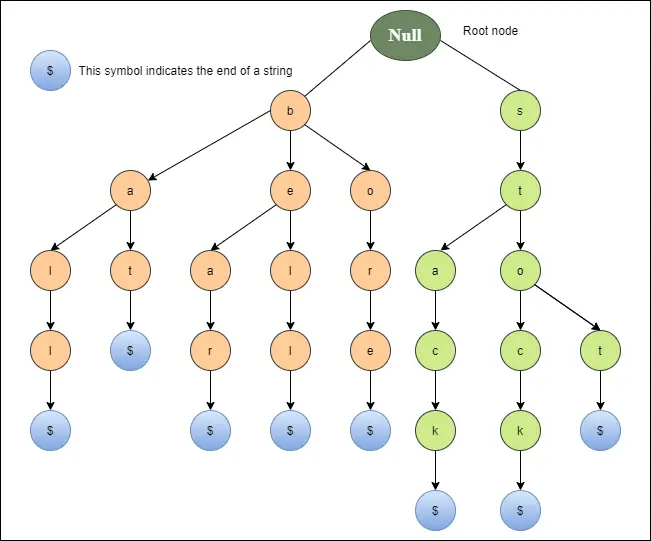
Základní operace Trie
V Trie jsou tři operace:
- Vložení uzlu
- Hledání uzlu
- Vymazání uzlu
Vložení uzlu do Trie
První operací je vložení nového uzlu do trie. Než začneme s implementací, je důležité porozumět některým bodům:
- Každé písmeno vstupního klíče (slova) se vloží jako jednotlivec do Trie_node. Všimněte si, že děti ukazují na další úroveň uzlů Trie.
- Pole klíčových znaků funguje jako index potomků.
- Pokud současný uzel již má odkaz na současné písmeno, nastavte současný uzel na tento odkazovaný uzel. V opačném případě vytvořte nový uzel, nastavte písmeno tak, aby se rovnalo současnému písmenu, a dokonce začněte současný uzel s tímto novým uzlem.
- Délka znaku určuje hloubku pokusu.
Implementace vložení nového uzlu do Trie
public class Data_Trie { private Node_Trie root; public Data_Trie(){ this.root = new Node_Trie(); } public void insert(String word){ Node_Trie current = root; int length = word.length(); for (int x = 0; x <length; x++){ char l="word.charAt(x);" node_trie node="current.getNode().get(L);" if (node="=" null){ (); current.getnode().put(l, node); } current="node;" current.setword(true); < pre> <h3>Searching a node in Trie</h3> <p>The second operation is to search for a node in a Trie. The searching operation is similar to the insertion operation. The search operation is used to search a key in the trie. The implementation of the searching operation is shown below.</p> <p>Implementation of search a node in the Trie</p> <pre> class Search_Trie { private Node_Trie Prefix_Search(String W) { Node_Trie node = R; for (int x = 0; x <w.length(); x++) { char curletter="W.charAt(x);" if (node.containskey(curletter)) node="node.get(curLetter);" } else return null; node; public boolean search(string w) node_trie !="null" && node.isend(); < pre> <h3>Deletion of a node in the Trie</h3> <p>The Third operation is the deletion of a node in the Trie. Before we begin the implementation, it is important to understand some points:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>If the key is not found in the trie, the delete operation will stop and exit it.</li> <li>If the key is found in the trie, delete it from the trie.</li> </ol> <p> <strong>Implementation of delete a node in the Trie</strong> </p> <pre> public void Node_delete(String W) { Node_delete(R, W, 0); } private boolean Node_delete(Node_Trie current, String W, int Node_index) { if (Node_index == W.length()) { if (!current.isEndOfWord()) { return false; } current.setEndOfWord(false); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } char A = W.charAt(Node_index); Node_Trie node = current.getChildren().get(A); if (node == null) { return false; } boolean Current_Node_Delete = Node_delete(node, W, Node_index + 1) && !node.isEndOfWord(); if (Current_Node_Delete) { current.getChildren().remove(A); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } return false; } </pre> <h2>Applications of Trie</h2> <p> <strong>1. Spell Checker</strong> </p> <p>Spell checking is a three-step process. First, look for that word in a dictionary, generate possible suggestions, and then sort the suggestion words with the desired word at the top.</p> <p>Trie is used to store the word in dictionaries. The spell checker can easily be applied in the most efficient way by searching for words on a data structure. Using trie not only makes it easy to see the word in the dictionary, but it is also simple to build an algorithm to include a collection of relevant words or suggestions.</p> <p> <strong>2. Auto-complete</strong> </p> <p>Auto-complete functionality is widely used on text editors, mobile applications, and the Internet. It provides a simple way to find an alternative word to complete the word for the following reasons.</p> <ul> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> <li>We trace pointers only to get the node that represents the string entered by the user.</li> <li>As soon as you start typing, it tries to complete your input.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>3. Browser history</strong> </p> <p>It is also used to complete the URL in the browser. The browser keeps a history of the URLs of the websites you've visited.</p> <h2>Advantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It can be insert faster and search the string than hash tables and binary search trees.</li> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> </ol> <h2>Disadvantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It requires more memory to store the strings.</li> <li>It is slower than the hash table.</li> </ol> <h2>Complete program in C++</h2> <pre> #include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - 'a'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" '�') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf('%c ', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf('search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf('not found
'); else printf('found!
'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" 'oh'); 'way'); 'bag'); 'can'); search(flag, 'ohh'); 'ways'); print_trie(flag); printf('
'); printf('deleting 'hello'...
'); 'can'...
'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;></pre></w.length();></pre></length;> Aplikace Trie
1. Kontrola pravopisu
Kontrola pravopisu se skládá ze tří kroků. Nejprve vyhledejte toto slovo ve slovníku, vygenerujte možné návrhy a poté seřaďte navrhovaná slova s požadovaným slovem nahoře.
logika prvního řádu
Trie se používá k uložení slova do slovníků. Kontrolu pravopisu lze snadno použít nejúčinnějším způsobem hledáním slov v datové struktuře. Použití trie nejen usnadňuje zobrazení slova ve slovníku, ale je také snadné sestavit algoritmus, který bude obsahovat sbírku relevantních slov nebo návrhů.
2. Automatické dokončování
Funkce automatického dokončování je široce používána v textových editorech, mobilních aplikacích a na internetu. Poskytuje jednoduchý způsob, jak najít alternativní slovo k doplnění slova z následujících důvodů.
- Poskytuje abecední filtr záznamů podle klíče uzlu.
- Trasujeme ukazatele pouze proto, abychom získali uzel, který představuje řetězec zadaný uživatelem.
- Jakmile začnete psát, pokusí se dokončit váš vstup.
3. Historie prohlížeče
výhody a nevýhody technologie
Používá se také k dokončení adresy URL v prohlížeči. Prohlížeč uchovává historii adres URL webových stránek, které jste navštívili.
Výhody Trie
- Lze jej vložit rychleji a prohledat řetězec než hashovací tabulky a binární vyhledávací stromy.
- Poskytuje abecední filtr záznamů podle klíče uzlu.
Nevýhody Trie
- Vyžaduje více paměti pro uložení řetězců.
- Je pomalejší než hashovací tabulka.
Kompletní program v C++
#include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - \'a\'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" \'�\') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - \'a\'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf(\'%c \', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf(\'search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf(\'not found
\'); else printf(\'found!
\'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" \'oh\'); \'way\'); \'bag\'); \'can\'); search(flag, \'ohh\'); \'ways\'); print_trie(flag); printf(\'
\'); printf(\'deleting \'hello\'...
\'); \'can\'...
\'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;> 