AVL strom:
AVL strom je samovyvažující binární vyhledávací strom ( BST ), kde rozdíl mezi výškami levého a pravého podstromu nemůže být větší než jeden pro všechny uzly.
Příklad stromu AVL:
Výše uvedený strom je AVL, protože rozdíly mezi výškami levého a pravého podstromu pro každý uzel jsou menší nebo rovné 1.
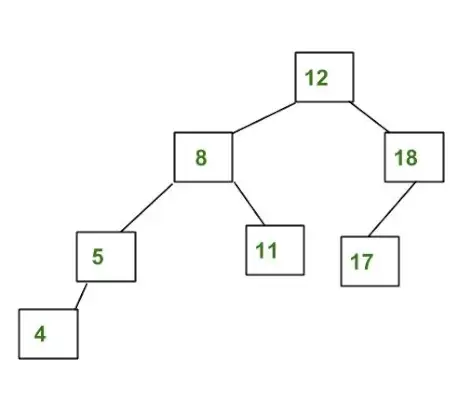
Příklad stromu, který NENÍ stromem AVL:

Výše uvedený strom není AVL, protože rozdíly mezi výškami levého a pravého podstromu pro 8 a 12 jsou větší než 1.
Proč AVL Trees?
Většina operací BST (např. vyhledávání, max., min., vkládání, mazání atd.) trvá Ach) čas kde h je výška BST. Náklady na tyto operace se mohou zvýšit Na) pro zkosený binární strom . Pokud dbáme na to, aby zůstala výška stromu O(log(n)) po každém vložení a smazání pak můžeme zaručit horní hranici O(log(n)) pro všechny tyto operace. Výška stromu AVL je vždy O(log(n)) kde n je počet uzlů ve stromu.
Vložení ve stromu AVL:
Abychom se ujistili, že daný strom zůstane AVL po každém vložení, musíme rozšířit standardní operaci vložení BST, abychom provedli určité vyrovnání.
Následují dvě základní operace, které lze provést pro vyvážení BST bez porušení vlastnosti BST (klávesy(vlevo)
- Levá rotace
- Pravá rotace
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 a / <- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>Doporučený postup Vkládání stromu AVL Vyzkoušejte to!
Postup při vkládání:
Nechte nově vložený uzel být v
- Proveďte standardní BST vložit pro v .
- Začínající od v , cestuj nahoru a najdi první nevyvážený uzel . Nechat S být prvním nevyváženým uzlem, a být dítě z S která přichází na cestu z v na S a X být vnouče z S která přichází na cestu z v na S .
- Znovu vyvažte strom provedením vhodných rotací na podstromu, který má kořeny S. Mohou existovat 4 možné případy, které je třeba řešit jako x, y a S lze uspořádat 4 způsoby.
- Zde jsou možná 4 uspořádání:
- y je levý potomek z a x je levý potomek y (levé levé písmeno)
- y je levý potomek z a x je pravý potomek y (levý a pravý případ)
- y je správným potomkem z a x je správným potomkem y (pravý správný případ)
- y je pravý potomek z a x je levý potomek y (pravý levý případ)
Následují operace, které je třeba provést ve výše uvedených 4 případech. Ve všech případech jen potřebujeme znovu vyvážit podstrom zakořeněný s S a celý strom se vyrovná podle výšky podstromu (po příslušné rotaci) zakořeněné S bude stejný jako před vložením.
1. Levé levé pouzdro
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->/ / x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. Left Right Case
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. Pravé Pravé pouzdro
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. Pravé levé pouzdro
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
Ilustrace vložení na strom AVL





Přístup:
Myšlenka je použít rekurzivní BST insert, po vložení dostaneme ukazatele na všechny předky jeden po druhém způsobem zdola nahoru. Takže nepotřebujeme rodičovský ukazatel, abychom mohli cestovat nahoru. Samotný rekurzivní kód putuje nahoru a navštíví všechny předky nově vloženého uzlu.
Při realizaci nápadu postupujte podle níže uvedených kroků:
- Proveďte normální vložení BST.
- Aktuální uzel musí být jedním z předků nově vloženého uzlu. Aktualizujte výška aktuálního uzlu.
- Získejte faktor rovnováhy (levá výška podstromu – pravá výška podstromu) aktuálního uzlu.
- Pokud je součinitel rovnováhy větší než 1, pak je aktuální uzel nevyvážený a my jsme buď v Levé levé pouzdro nebo levé Pravé pouzdro . Chcete-li zkontrolovat, zda je levé levé pouzdro nebo ne, porovnejte nově vložený klíč s klíčem v levý kořen podstromu .
- Pokud je bilanční faktor menší než -1 , pak je aktuální uzel nevyvážený a jsme buď v případě Right Right nebo Right-Left. Chcete-li zkontrolovat, zda se jedná o případ Right Right nebo ne, porovnejte nově vložený klíč s klíčem v pravém kořeni podstromu.
Níže je uvedena implementace výše uvedeného přístupu:
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->výška;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->klíč = klíč;> >node->vlevo = NULL;> >node->vpravo = NULL;> >node->výška = 1;>// new node is initially> >// added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->vlevo, odjet;> >Node *T2 = x->že jo;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->vpravo = y;> >y->vlevo = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y->výška = max(výška(y->vlevo),> >height(y->vpravo)) + 1;> >x->výška = max(výška(x->vlevo),> >height(x->vpravo)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->že jo;> >Node *T2 = y->vlevo, odjet;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->vlevo = x;> >x->vpravo = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x->výška = max(výška(x->vlevo),> >height(x->vpravo)) + 1;> >y->výška = max(výška(y->vlevo),> >height(y->vpravo)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->vlevo) - výška(N->vpravo);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(uzel->left, key);> >else> if> (key>uzel->klíč)> >node->right = insert(uzel->right, key);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->výška = 1 + max(výška(uzel->vlevo),> >height(node->že jo));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 klávesa && vlevo->klávesa)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->vpravo->klávesa)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 klávesa &&> uzel->vlevo->klávesa)> >{> >node->doleva = dolevaRotate(uzel->vlevo);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->klíč)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(uzel->right);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->vlevo, odjet); preOrder(root->right); } } // Kód ovladače int main() { Uzel *root = NULL; /* Konstrukce stromu na obrázku výše */ root = insert(root, 10); root = insert(kořen, 20); root = insert(kořen, 30); root = insert(kořen, 40); root = insert(root, 50); root = insert(kořen, 25); /* Konstruovaný strom AVL by byl 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->výška;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->klíč = klíč;> >node->vlevo = NULL;> >node->vpravo = NULL;> >node->výška = 1;>// new node is initially added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->vlevo, odjet;> >struct> Node *T2 = x->že jo;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->vpravo = y;> >y->vlevo = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y->výška = max(výška(y->vlevo),> >height(y->vpravo)) + 1;> >x->výška = max(výška(x->vlevo),> >height(x->vpravo)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->že jo;> >struct> Node *T2 = y->vlevo, odjet;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->vlevo = x;> >x->vpravo = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x->výška = max(výška(x->vlevo),> >height(x->vpravo)) + 1;> >y->výška = max(výška(y->vlevo),> >height(y->vpravo)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->vlevo) - výška(N->vpravo);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(uzel->left, key);> >else> if> (key>uzel->klíč)> >node->right = insert(uzel->right, key);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->výška = 1 + max(výška(uzel->vlevo),> >height(node->že jo));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 klávesa && vlevo->klávesa)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->vpravo->klávesa)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 klávesa &&> uzel->vlevo->klávesa)> >{> >node->left = leftRotate(uzel->left);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->klíč)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(uzel->right);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->klíč);> >preOrder(root->vlevo, odjet);> >preOrder(root->že jo);> >}> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Jáva
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>b) ? a: b;> >}> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(uzel.right, key); else // Duplicitní klíče nejsou povoleny návratový uzel; /* 2. Aktualizace výšky tohoto uzlu předka */ node.height = 1 + max(height(uzel.left), height(uzel.right)); /* 3. Získejte faktor rovnováhy tohoto předchůdce, abyste zjistili, zda tento uzel není nevyvážený */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Pokud se tento uzel stane nevyváženým, jsou zde // 4 případy Left Left Case if (zůstatek> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance<-1 && key>node.right.key) return leftRotate(uzel); // Left Right Case if (zůstatek> 1 && klíč> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(uzel); } // Right Left Case if (balance<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
Python3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 a klíč se vrátí self.rightRotate(root) # Případ 2 - Right Right při vyvážení<-1 and key>root.right.val: return self.leftRotate(root) # Případ 3 - Left Right if balance> 1 and key> root.left.val: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root ) # Případ 4 - Pravý Levý při vyvážení<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
C#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>b) ? a: b;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(uzel.right, key); else // Duplicitní klíče nejsou povoleny návratový uzel; /* 2. Aktualizace výšky tohoto uzlu předka */ node.height = 1 + max(height(uzel.left), height(uzel.right)); /* 3. Získejte faktor rovnováhy tohoto předchůdce, abyste zjistili, zda tento uzel není nevyvážený */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Pokud se tento uzel stane nevyváženým, jsou zde // 4 případy Left Left Case if (zůstatek> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) return leftRotate(node) ; // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(uzel.left return rightRotate(uzel);<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
Javascript
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>b ? a: b;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = this.insert(uzel.right, key); // Duplicitní klíče nejsou povoleny else return node; /* 2. Aktualizace výšky tohoto uzlu předka */ node.height = 1 + this.max(this.height(uzel.left), this.height(uzel.right)); /* 3. Získejte faktor rovnováhy tohoto předchůdce, abyste zjistili, zda tento uzel není nevyvážený */ var balance = this.getBalance(node); // Pokud se tento uzel stane nevyváženým, jsou zde // 4 případy Left Left Case if (zůstatek> 1 klávesa && return this.rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) vrátí toto. leftRotate(node) // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = this.leftRotate(uzel.left return this.rightRotate(node); Levý případ, pokud (zůstatek<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root); > |
>
>Výstup
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
Analýza složitosti
Časová náročnost: O(log(n)), pro vložení
Pomocný prostor: O(1)
ukázkové programy java
Operace otáčení (otáčení doleva a doprava) trvá konstantní čas, protože se zde mění pouze několik ukazatelů. Aktualizace výšky a získání faktoru vyvážení také trvá konstantní čas. Časová složitost vložky AVL tedy zůstává stejná jako vložka BST, což je O(h), kde h je výška stromu. Protože je strom AVL vyvážený, výška je O(Logn). Časová složitost vložky AVL je tedy O(Logn).
Srovnání s Red Black Tree:
Strom AVL a další samovyvažující vyhledávací stromy, jako je Red Black, jsou užitečné k provádění všech základních operací v čase O(log n). Stromy AVL jsou vyváženější ve srovnání s stromy Red-Black Trees, ale mohou způsobit více rotací během vkládání a mazání. Pokud tedy vaše aplikace zahrnuje mnoho častých vkládání a mazání, měly by být preferovány stromy Red Black. A pokud jsou vkládání a mazání méně časté a vyhledávání je častější operací, pak by měl být strom AVL preferován před Red Black Tree .
Následuje příspěvek ke smazání ve stromu AVL:
AVL strom | Sada 2 (smazání)
