Vzhledem k souboru měst a vzdálenosti mezi každou dvojicí měst je problém najít nejkratší možnou turné, které navštíví každé město přesně jednou a vrací se do výchozího bodu.
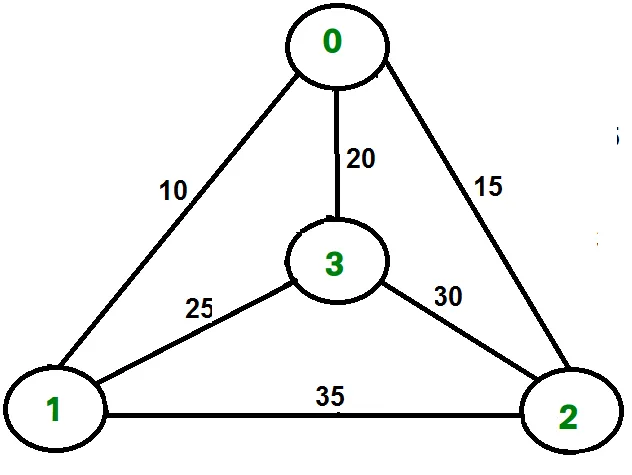
Například zvažte graf zobrazený na obrázku na pravé straně. Prohlídka TSP v grafu je 0-1-3-2-0. Náklady na prohlídku jsou 10+25+30+15, což je 80.
Diskutovali jsme následující řešení
1) Naivní a dynamické programování
2) Přibližné řešení pomocí MST
Větev a vázané řešení
Jak je vidět v předchozích článcích v pobočce a vázané metodě pro aktuální uzel ve stromu, vypočítáme vázání nejlepšího možného řešení, které můžeme získat, pokud dojde k tomuto uzlu. Pokud je svázané na samotném nejlepším možném řešení horší než nejlepší nejlepší (dosud nejlépe vypočítané), ignorujeme podstrom zakořeněný s uzlem.
Všimněte si, že náklady prostřednictvím uzlu zahrnují dvě náklady.
1) Náklady na dosažení uzlu z kořene (když dosáhneme uzlu, máme tyto náklady vypočteny)
2) Náklady na dosažení odpovědi z aktuálního uzlu na list (vypočítáme vázání této náklady, abychom rozhodli, zda ignorovat podstrom s tímto uzlem nebo ne).
- V případě a Problém maximalizace Horní hranice nám říká maximální možné řešení, pokud budeme sledovat daný uzel. Například v 0/1 Knapsack Použili jsme chamtivý přístup k nalezení horní hranice .
- V případě a Minimalizační problém Dolní hranice nám říká minimální možné řešení, pokud budeme sledovat daný uzel. Například v Problém při přiřazení práce Dostaneme spodní hranici přiřazením úlohy s nejmenšími náklady pracovníkovi.
V pobočce a svázaná náročnou část je vymyslet způsob, jak vypočítat svázaní na nejlepší možné řešení. Níže je myšlenka, která se používá k výpočtu hranic problému pro prodejce.
Náklady na jakoukoli prohlídku lze napsat níže.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Například zvažte výše uvedený graf. Níže jsou uvedeny minimální náklady na dva hrany sousedící s každým uzlem.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Nyní máme představu o výpočtu dolní hranice. Podívejme se, jak to, jak jej aplikovat strom vyhledávání stavu. Začneme vyjmenování všech možných uzlů (nejlépe v lexikografickém pořadí)
1. Kořenový uzel: Bez ztráty obecnosti předpokládáme, že začneme na vrcholu „0“, pro které byla spodní hranice vypočtena výše.
Řešení úrovně 2: Další úroveň vyjmenovává všechny možné vrcholy, ke kterým můžeme jít (s ohledem na to, že v jakékoli cestě se vrchol musí nastat pouze jednou), které jsou 1 2 3 ... n (všimněte si, že graf je kompletní). Zvažte, že počítáme pro vrchol 1, protože jsme se přesunuli z 0 na 1, naše turné nyní zahrnovalo Edge 0-1. To nám umožňuje provádět nezbytné změny v dolní hranici kořene.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Jak to funguje? Abychom zahrnuli hranu 0-1, přidáme okrajové náklady 0-1 a odečtěte hran Hmotnost tak, že spodní hranice zůstává co nejvíce těsná, což by bylo součtem minimálních okrajů 0 a 1 děleno 2. Jasně odečteno hranou odečteno menší než toto.
Řešení s jinými úrovními: Když přecházíme na další úroveň, znovu vyjmenujeme všechny možné vrcholy. Pro výše uvedený případ jde dále po 1 zkontrolovat 2 3 4 ... n.
Zvažte dolní hranici pro 2, když jsme se přesunuli z 1 na 1, zahrnujeme hranu 1-2 na turné a změníme nový dolní mez pro tento uzel.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
Poznámka: Jedinou změnou ve vzorci je, že tentokrát jsme zahrnuli druhé minimální náklady na hranu za 1, protože minimální náklady na okraj již byly odečteny v předchozí úrovni.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include
// Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.*; class GFG { static int N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path[] = new int[N + 1]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited[] = new boolean[N]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal(int curr_path[]) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin(int adj[][] int i) { int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) if (adj[i][k] < min && i != k) min = adj[i][k]; return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin(int adj[][] int i) { int first = Integer.MAX_VALUE second = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (adj[i][j] <= first) { second = first; first = adj[i][j]; } else if (adj[i][j] <= second && adj[i][j] != first) second = adj[i][j]; } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec(int adj[][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path[]) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] != 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level-1]][curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal(curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if (adj[curr_path[level-1]][i] != 0 && visited[i] == false) { int temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res) { curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level-1]][i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array Arrays.fill(visitedfalse); for (int j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP(int adj[][]) { int curr_path[] = new int[N + 1]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0; Arrays.fill(curr_path -1); Arrays.fill(visited false); // Compute initial bound for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = (curr_bound==1)? curr_bound/2 + 1 : curr_bound/2; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj[][] = {{0 10 15 20} {10 0 35 25} {15 35 0 30} {20 25 30 0} }; TSP(adj); System.out.printf('Minimum cost : %dn' final_res); System.out.printf('Path Taken : '); for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { System.out.printf('%d ' final_path[i]); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
# Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float('inf') # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal(curr_path): final_path[:N + 1] = curr_path[:] final_path[N] = curr_path[0] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin(adj i): min = maxsize for k in range(N): if adj[i][k] < min and i != k: min = adj[i][k] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin(adj i): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range(N): if i == j: continue if adj[i][j] <= first: second = first first = adj[i][j] elif(adj[i][j] <= second and adj[i][j] != first): second = adj[i][j] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N: # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] != 0: # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1]] [curr_path[0]] if curr_res < final_res: copyToFinal(curr_path) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range(N): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if (adj[curr_path[level-1]][i] != 0 and visited[i] == False): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1: curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2) else: curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res: curr_path[level] = i visited[i] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [False] * len(visited) for j in range(level): if curr_path[j] != -1: visited[curr_path[j]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP(adj): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [-1] * (N + 1) visited = [False] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range(N): curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math.ceil(curr_bound / 2) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = True curr_path[0] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[0 10 15 20] [10 0 35 25] [15 35 0 30] [20 25 30 0]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [None] * (N + 1) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [False] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP(adj) print('Minimum cost :' final_res) print('Path Taken : ' end = ' ') for i in range(N + 1): print(final_path[i] end = ' ') # This code is contributed by ng24_7
// C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System; public class GFG { static int N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int[] final_path = new int[N + 1]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool[] visited = new bool[N]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32.MaxValue; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal(int[] curr_path) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin(int[ ] adj int i) { int min = Int32.MaxValue; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) if (adj[i k] < min && i != k) min = adj[i k]; return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin(int[ ] adj int i) { int first = Int32.MaxValue second = Int32.MaxValue; for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (adj[i j] <= first) { second = first; first = adj[i j]; } else if (adj[i j] <= second && adj[i j] != first) second = adj[i j]; } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec(int[ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int[] curr_path) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1] curr_path[0]] != 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1] curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal(curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if (adj[curr_path[level - 1] i] != 0 && visited[i] == false) { int temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1] i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level == 1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res) { curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1] i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array Array.Fill(visited false); for (int j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP(int[ ] adj) { int[] curr_path = new int[N + 1]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0; Array.Fill(curr_path -1); Array.Fill(visited false); // Compute initial bound for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = (curr_bound == 1) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } // Driver code static public void Main() { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int[ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP(adj); Console.WriteLine('Minimum cost : ' + final_res); Console.Write('Path Taken : '); for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { Console.Write(final_path[i] + ' '); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
const N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array (N + 1).fill (-1); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array (N).fill (false); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal (curr_path){ for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; } final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin (adj i){ let min = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let k = 0; k < N; k++){ if (adj[i][k] < min && i !== k){ min = adj[i][k]; } } return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin (adj i){ let first = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; let second = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let j = 0; j < N; j++){ if (i == j){ continue; } if (adj[i][j] <= first){ second = first; first = adj[i][j]; } else if (adj[i][j] <= second && adj[i][j] !== first){ second = adj[i][j]; } } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec (adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] !== 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal (curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] !== 0 && !visited[i]){ let temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level == 1){ curr_bound -= (firstMin (adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin (adj i)) / 2; } else { curr_bound -= (secondMin (adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin (adj i)) / 2; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res){ curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec (adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array visited.fill (false) for (var j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP (adj) { let curr_path = Array (N + 1).fill (-1); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0; visited.fill (false); // compute initial bound for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ curr_bound += firstMin (adj i) + secondMin (adj i); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? (curr_bound / 2) + 1 : (curr_bound / 2); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec (adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj =[[0 10 15 20] [10 0 35 25] [15 35 0 30] [20 25 30 0]]; TSP (adj); console.log (`Minimum cost:${final_res}`); console.log (`Path Taken:${final_path.join (' ')}`); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Výstup:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Zaokrouhlování se provádí v této linii kódu:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
V algoritmu větve a vázaného TSP vypočítáme spodní hranici celkových nákladů na optimální řešení přidáním minimálních okrajových nákladů pro každý vrchol a poté rozdělením dvěma. Tato spodní hranice však nemusí být celé číslo. K získání celého celého celého hranice můžeme použít zaokrouhlení.
Ve výše uvedeném kódu drží proměnná Curr_bound aktuální spodní hranice celkových nákladů na optimální řešení. Když navštívíme nový vrchol na úrovni úrovně, vypočítáme nový dolní vázaný New_bound tím, že vezmeme částku minimálních nákladů na hranu pro nový vrchol a jeho dva nejbližší sousedy. Poté aktualizujeme proměnnou Curr_Bound zaokrouhlením new_bound na nejbližší celé číslo.
Pokud je úroveň 1, zaokrouhlíme dolů na nejbližší celé číslo. Je to proto, že jsme dosud navštívili pouze jeden vrchol a chceme být konzervativní v našem odhadu celkových nákladů na optimální řešení. Pokud je úroveň větší než 1, používáme agresivnější strategii zaoblení, která bere v úvahu skutečnost, že jsme již navštívili některé vrcholy, a proto můžeme provést přesnější odhad celkových nákladů na optimální řešení.
Složitost času: Nejhorší složitost větve a vázání zůstává stejná jako složitost brutální síly jasně, protože v nejhorším případě možná nikdy nebudeme mít šanci prořezávat uzel. Zatímco v praxi to funguje velmi dobře v závislosti na různých případech TSP. Složitost také závisí na výběru ohraničovací funkce, protože jsou ti, kteří rozhodují, kolik uzlů má být ořezáno.
Reference:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html
