std::shared_ptr je jedním z chytrých ukazatelů představených v C++11. Na rozdíl od jednoduchého ukazatele má přidružený řídicí blok, který sleduje počet odkazů pro spravovaný objekt. Tento počet referencí je sdílen mezi všemi kopiemi instancí shared_ptr směřujících na stejný objekt, což zajišťuje správnou správu paměti a mazání.
Předpoklady: Ukazatele v C++ , Inteligentní ukazatele v C++ .
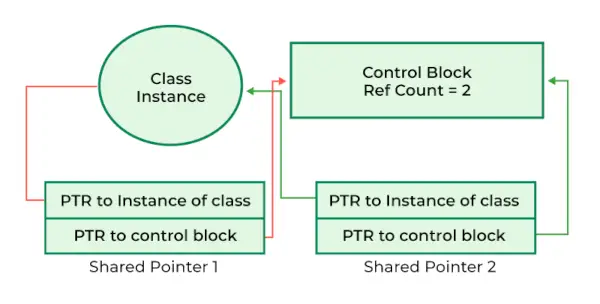
Sdílený ukazatel v C++
Syntaxe std::shared_ptr
Shared_ptr typu T lze deklarovat jako:
std::shared_ptr ptr_name;>
Inicializace objektů shared_ptr
Sdílený_ptr můžeme inicializovat pomocí následujících metod:
1. Inicializace pomocí nového ukazatele
shared_ptr ptr (new T()); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared (new T());>
2. Inicializace pomocí existujícího ukazatele
shared_ptr ptr(already_existing_pointer); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared(already_existing_pointer);>
Členské metody sdílené_ptr
Následuje několik členů spojených s shared_ptr:
| Metoda | Popis |
|---|---|
| reset() | Resetuje std::shared_ptr na prázdnou, čímž uvolní vlastnictví spravovaného objektu. |
| use_count() | Vrátí aktuální počet referencí udávající, kolik instancí std::shared_ptr sdílí vlastnictví. |
| unikátní() | Zkontrolujte, zda objekt vlastní pouze jeden std::shared_ptr (počet referencí je 1). |
| dostat() | Vrátí nezpracovaný ukazatel na spravovaný objekt. Při používání této metody buďte opatrní. |
| swap(shr_ptr2) | zamění obsah (vlastnictví) dvou instancí std::shared_ptr. |
Příklady std::shared_ptr
Příklad 1:
C++
>
>Výstup
0x1365c20 A::show() A::show() 0x1365c20 0x1365c20 2 2 0 1 0x1365c20>
Příklad 2:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the use of make_shared> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> >// Creating shared pointers using std::make_shared> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr1 = make_shared<>int>>(42);> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr2 = make_shared<>int>>(24);> >// Accessing the values using the dereference operator> >// (*)> >cout << 'Value 1: ' << *shr_ptr1 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 2: ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >// Using the assignment operator (=) to share ownership> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr3 = shr_ptr1;> >// Checking if shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3> >// point to the same object> >if> (shr_ptr1 == shr_ptr3) {> >cout << 'shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 '> >'point to the same object.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Swapping the contents of shared pointer 2 and shared> >// pointer 3> >shr_ptr2.swap(shr_ptr3);> >// Checking the values after the swap> >cout << 'Value 2 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 3 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr3 << endl;> >// Using logical operators to check if shared pointers> >// are valid> >if> (shr_ptr1 && shr_ptr2) {> >cout << 'Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer '> >'2 are valid.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Resetting a shared pointer> >shr_ptr1.reset();> }> |
>
>Výstup
Value 1: 42 Value 2: 24 shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 point to the same object. Value 2 (after swap): 42 Value 3 (after swap): 24 Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 2 are valid.>
Příklad 3: Implementace propojeného seznamu pomocí std::shared_ptr
C++
#include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Define a singly linked list node> struct> Node {> >int> data;> >shared_ptr next;> >Node(>int> val)> >: data(val)> >, next(NULL)> >{> >}> };> class> LinkedList {> public>:> >LinkedList()> >: head(NULL)> >{> >}> >// Insert a new node at the end of the linked list> >void> insert(>int> val)> >{> >shared_ptr newNode = make_shared(val);> >if> (!head) {> >head = newNode;> >}> >else> {> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->další) {> >current = current->další;> >}> >current->next = newNode;> >}> >}> >// Delete a node with a given value from the linked list> >void> del(>int> val)> >{> >if> (!head) {> >return>;> >}> >if> (head->data == val) {> >head = head->další;> >return>;> >}> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->další> >&& current->další->data != val) {> >current = current->další;> >}> >if> (current->další && aktuální->další->data == val) {> >current->další = aktuální->další->další;> >}> >}> >// Traverse and print the linked list> >void> Print()> >{> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current) {> >cout current = current->další; } cout<< 'NULL' << endl; } private: shared_ptr head; }; int main() { LinkedList linkedList; // Insert nodes into the linked list linkedList.insert(1); linkedList.insert(2); linkedList.insert(3); // Print the linked list cout << 'Linked List: '; linkedList.Print(); // Delete a node and print the updated linked list linkedList.del(2); cout << 'Linked List after deleting 2: '; linkedList.Print(); return 0; }> |
>
html tagy
>Výstup
