Můžeme vytvořit java program pro třídění prvků pole pomocí výběrového třídění. V algoritmu třídění výběru hledáme nejnižší prvek a uspořádáme jej na správné místo. Vyměníme aktuální prvek za další nejnižší číslo.
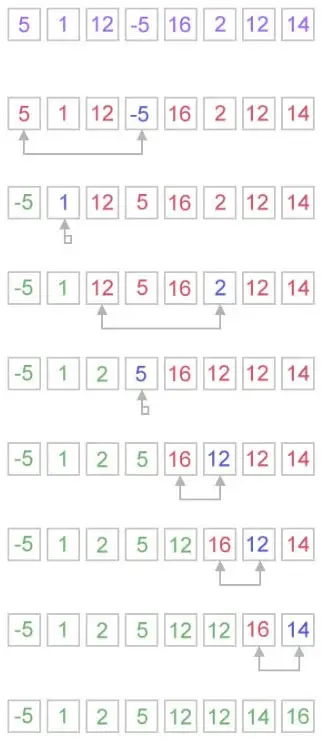
Jak funguje výběrové řazení?
Algoritmus řazení výběru funguje velmi jednoduchým způsobem. Udržuje dvě podpole pro dané pole.
strojopis každý
- Podpole je již seřazeno.
- A druhé podpole je neseřazené.
Při každé iteraci třídění výběru je prvek vybrán z netříděného podpole a přesunut do tříděného podpole.
příklady operačních systémů
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Časová složitost
Nejlepší: ?(n^2)Průměrný: ?(n^2)
Nejhorší: O(n^2)
Vesmírná složitost
O(1)Výběr Třídění Java Příklad
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Třídění výběru v Javě (jiný způsob)
Můžete také použít metodu, kde pole není předdefinováno. Zde musí uživatel vložit prvky jako vstup.
V následujícím programu Java požádáme uživatele, aby zadal prvky pole nebo číslo, nyní porovnejte prvek pole a začněte swapovat s proměnnou temp. Vložte první prvek do temp a druhý prvek do prvního a potom temp do druhého čísla a pokračujte pro další shodu, aby se celé pole seřadilo vzestupně.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>