Vzhledem k tomu obdélníkový papír o rozměrech a x b . Úkolem je rozřezat celý papír minimální počet náměstí kusy. Můžeme si vybrat čtvercové kusy libovolné velikosti, ale musí být nakrájeny aniž by se překrývaly nebo ponechaly prostor navíc .
řetězení řetězců
Příklady:
Vstup: a = 5 b = 8
5 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 5 X 8
výstup: 5
Vysvětlení: Papír můžeme rozstříhat na 5 čtverců: 1 čtverec o velikosti 5x5 1 čtverec o velikosti 3x3 1 čtverec o velikosti 2x2 a 2 čtverce o velikosti 1x1.Vstup: a = 13 b = 11
6 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 13 X 11
výstup: 6
Vysvětlení: Papír můžeme rozstříhat na 6 čtverců: 1 čtverec o velikosti 7x7 1 čtverec o velikosti 6x6 1 čtverec o velikosti 5x5 2 čtverce o velikosti 4x4 a 1 čtverec o velikosti 1x1.gzip pro linuxVstup: a = 6 b = 7
5 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 6 X 7
výstup: 5
Vysvětlení: Papír můžeme rozstříhat na 5 čtverců: 1 čtverec o velikosti 4x4 2 čtverce o velikosti 3x3 a 2 čtverce o velikosti 3x3.
Obsah
- [Nesprávný přístup 1] Použití chamtivé techniky
- [Nesprávný přístup 2] Použití dynamického programování
- [Správný přístup] Pomocí DFS a dynamického programování
[Nesprávný přístup 1] Použití chamtivé techniky
Na první pohled by se mohlo zdát, že problém lze snadno vyřešit tak, že z papíru nejprve vystřihneme co největší čtverec a poté ze zbývajícího papíru vystřihneme největší čtverec a tak dále, dokud papír neořízneme celý. Toto řešení je ale nesprávné.
Proč Greedy Approach nefunguje?
Zvažte papír velikosti 6x7 pak když se pokusíme papír hltavě řezat, dostaneme 7 čtverce: 1 čtverec velikosti 6x6 a 6 čtverců o velikosti 1x1 přičemž správné řešení je: 5. Zištný přístup tedy nebude fungovat.
amisha Patel
[Nesprávný přístup 2] Použití dynamického programování
Dynamické programování s vertikálními nebo horizontálními řezy: Dalším řešením, které se může zdát správné, je použití Dynamické programování . Můžeme udržovat tabulku dp[][] takovou, že dp[i][j] = minimální počet čtverců, které lze vyříznout z papíru o velikosti i x j . Pak pro papír velikosti axb
porovnat s javou
- Můžeme to zkusit oříznout podél každého řádku: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) kde k může být v rozmezí [1 i - 1].
- Můžeme to zkusit oříznout podél každého sloupce: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) kde k může být v rozsahu [1 j - 1].
Nakonec bude odpovědí minimum všech řezů. Toto řešení je ale také nesprávné.
Proč řezání svisle nebo vodorovně s přístupem dynamického programování nefunguje?
To nebude fungovat, protože předpokládáme, že vertikální nebo horizontální řez vždy rozdělí obdélník na dvě části. Zvažte papír velikosti 13x11 pak, když se pokusíme oříznout papír pomocí DP přístupu, dostaneme 8 čtverců, ale správná odpověď (jak je ukázáno v příkladech) je 6. Dynamické programování tedy nebude fungovat.
[Správný přístup] Pomocí DFS a dynamického programování
C++The nápad je ořezat celý papír pomocí DFS v zdola nahoru způsob. V každém kroku najděte nejnižší levý roh papíru a pokuste se z tohoto rohu vyříznout čtverce všech možných velikostí. Po vyříznutí čtverce znovu najděte levý nejnižší roh zbývajícího papíru, abyste mohli vyřezat čtverce všech možných velikostí a tak dále. Ale pokud bychom zkoušeli všechny možné řezy od nejnižšího levého rohu každé možné velikosti papíru, pak by to bylo docela neefektivní. Můžeme ji optimalizovat pomocí Dynamické programování pro uložení minimálních řezů pro každou možnou velikost papíru.
Pro jednoznačnou identifikaci jakékoli velikosti papíru můžeme udržovat pole remSq[] tak, že remSq[i] ukládá počet zbývajících čtverců o velikosti 1x1 v i-tém sloupci papíru. Tedy pro papír o velikosti 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Abychom našli nejnižší levý roh, najdeme první index s maximálním počtem zbývajících čtverců. Můžeme tedy hashovat hodnotu pole remSq[], abychom našli jedinečný klíč pro všechny možné hodnoty pole remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Výstup
6
Časová složitost: O(a^b) pro každý z b sloupců můžeme mít čtverce.
Pomocný prostor: O(a^b) díky zapamatování ukládajícím každý jedinečný stav.

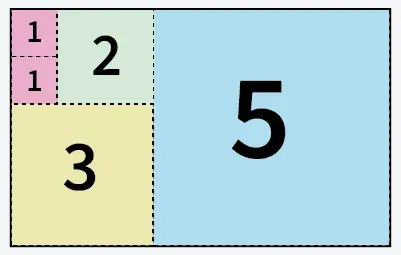 5 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 5 X 8
5 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 5 X 8 6 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 13 X 11
6 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 13 X 11 5 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 6 X 7
5 čtverců vystřižených z papíru o velikosti 6 X 7