Minimax je druh backtrackingového algoritmu, který se používá při rozhodování a teorii her k nalezení optimálního pohybu pro hráče za předpokladu, že váš soupeř také hraje optimálně. Je široce používán v tahových hrách pro dva hráče, jako jsou Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, šachy atd.
V Minimax se tito dva hráči nazývají maximalizér a minimalizátor. The maximalizátor se snaží získat co nejvyšší možné skóre minimalizátor se snaží udělat opak a získat co nejnižší skóre.
Každý stav desky má spojenou hodnotu. V daném stavu, pokud má maximalizér navrch, bude mít skóre na desce tendenci mít nějakou kladnou hodnotu. Pokud má minimalizátor v tomto stavu desky navrch, bude mít tendenci mít nějakou zápornou hodnotu. Hodnoty herního plánu se počítají pomocí nějaké heuristiky, která je jedinečná pro každý typ hry.
Příklad:
Představte si hru, která má 4 konečné stavy a cesty k dosažení konečného stavu jsou od kořene po 4 listy dokonalého binárního stromu, jak je ukázáno níže. Předpokládejme, že jste maximalizující hráč a máte první šanci se pohnout, tedy že jste u kořene a váš protivník na další úrovni. Jaký tah byste jako maximalizující hráč udělal s ohledem na to, že i váš soupeř hraje optimálně?
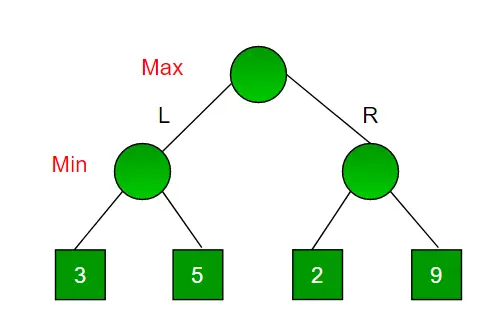
Vzhledem k tomu, že se jedná o algoritmus založený na backtrackingu, zkouší všechny možné pohyby, poté ustoupí a rozhodne se.
- Maximizer jde DOLEVA: Nyní jsou na řadě minimalizátory. Minimalizátor má nyní na výběr mezi 3 a 5. Jako minimalizátor si určitě vybere nejméně z obou, tedy 3
- Maximalizátor jde VPRAVO: Nyní jsou na řadě minimalizátory. Minimalizátor má nyní na výběr mezi 2 a 9. Zvolí 2, protože je to nejmenší ze dvou hodnot.
Jako maximalizér byste zvolili větší hodnotu, která je 3. Optimální pohyb pro maximalizér je tedy jít DOLEVA a optimální hodnota je 3.
Nyní strom hry vypadá takto:

základní otázky java interview
Výše uvedený strom ukazuje dvě možná skóre, když maximalizér provádí pohyby doleva a doprava.
Poznámka: I když je v pravém podstromu hodnota 9, minimalizátor ji nikdy nevybere. Vždy musíme vycházet z toho, že soupeř hraje optimálně.
Níže je implementace pro totéž.
C++
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Jáva
mapový strojopis
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
shloka mehta
>
C#
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
>
>
Python3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
Javascript
abeceda číslovaná
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
>
Výstup:
The optimal value is: 12>
Časová složitost: O(b^d) b je faktor větvení a d je počet hloubky nebo vrstvy grafu nebo stromu.
Prostorová složitost: O(bd) kde b je faktor větvení do d je maximální hloubka stromu podobná DFS.
Myšlenkou tohoto článku je představit Minimax na jednoduchém příkladu.
- Ve výše uvedeném příkladu má hráč pouze dvě možnosti. Obecně může být více možností. V takovém případě musíme opakovat všechny možné tahy a najít maximum/minimum. Například v Tic-Tac-Toe může první hráč provést 9 možných tahů.
- Ve výše uvedeném příkladu jsou nám přidělena skóre (listy stromu hry). Pro typickou hru musíme tyto hodnoty odvodit
Brzy pokryjeme Tic Tac Toe algoritmem Minimax.
K tomuto článku přispěl Akshay L. Aradhya.
příkaz arp-a
