Smyčky v programování se používají k opakování bloku kódu, dokud není splněna zadaná podmínka. Příkaz smyčky umožňuje programátorům provést příkaz nebo skupinu příkazů vícekrát bez opakování kódu.
pawandeep rajan
C
příkaz java return
// C program to illustrate need of loops> #include> > int> main()> {> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
co je ymail
>Výstup
Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World>
V programování C existují hlavně dva typy smyček:
apurva padgaonkar
- Vstupní řízené smyčky: Ve vstupních řízených smyčkách je testovací stav kontrolován před vstupem do hlavního tělesa smyčky. For Loop a While Loop je vstupní řízená smyčka. Exit Controlled loops: V Exit řízených smyčkách je testovací podmínka vyhodnocena na konci těla smyčky. Tělo smyčky se provede alespoň jednou, bez ohledu na to, zda je podmínka pravdivá nebo nepravdivá. do-while Loop je Exit Controlled loop.
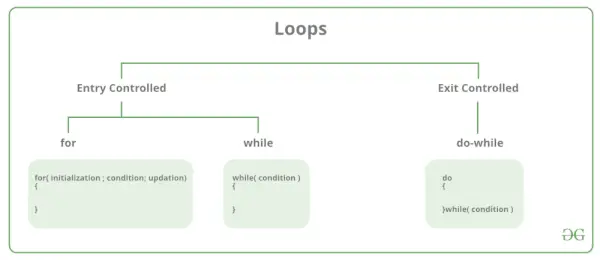
| Typ smyčky | Popis |
|---|---|
| pro smyčku | nejprve se inicializuje, poté zkontroluje stav, poté provede tělo a nakonec se provede aktualizace. |
| zatímco smyčka | nejprve Inicializuje, poté zkontroluje podmínky a poté provede tělo a aktualizace může být uvnitř těla. |
| smyčka do-while | do-while nejprve provede tělo a poté se provede kontrola stavu. |
pro Loop
Smyčka for v programování v jazyce C je struktura řízení opakování, která umožňuje programátorům napsat smyčku, která se provede určitý počet opakování. Smyčka for umožňuje programátorům provést n počet kroků společně na jednom řádku.
Syntax:
for (initialize expression; test expression; update expression) { // // body of for loop // }> Příklad:
for(int i = 0; i In for loop, a loop variable is used to control the loop. Firstly we initialize the loop variable with some value, then check its test condition. If the statement is true then control will move to the body and the body of for loop will be executed. Steps will be repeated till the exit condition becomes true. If the test condition will be false then it will stop. Initialization Expression: In this expression, we assign a loop variable or loop counter to some value. for example: int i=1; Test Expression: In this expression, test conditions are performed. If the condition evaluates to true then the loop body will be executed and then an update of the loop variable is done. If the test expression becomes false then the control will exit from the loop. for example, i<=9; Update Expression: After execution of the loop body loop variable is updated by some value it could be incremented, decremented, multiplied, or divided by any value. for loop Equivalent Flow Diagram: Example: C // C program to illustrate for loop #include // Driver code int main() { int i = 0; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { printf( 'Hello World
'); } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World While Loop While loop does not depend upon the number of iterations. In for loop the number of iterations was previously known to us but in the While loop, the execution is terminated on the basis of the test condition. If the test condition will become false then it will break from the while loop else body will be executed. Syntax: initialization_expression; while (test_expression) { // body of the while loop update_expression; } Flow Diagram for while loop: C // C program to illustrate // while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; // Test expression while(i <10) { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // update expression i++; } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World do-while Loop The do-while loop is similar to a while loop but the only difference lies in the do-while loop test condition which is tested at the end of the body. In the do-while loop, the loop body will execute at least once irrespective of the test condition. Syntax: initialization_expression; do { // body of do-while loop update_expression; } while (test_expression); C // C program to illustrate // do-while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; do { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // Update expression i++; // Test expression } while (i <1); return 0; } Output Hello World Above program will evaluate (i<1) as false since i = 2. But still, as it is a do-while loop the body will be executed once. Loop Control Statements Loop control statements in C programming are used to change execution from its normal sequence. Name Description break statement the break statement is used to terminate the switch and loop statement. It transfers the execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch. continue statement continue statement skips the remainder body and immediately resets its condition before reiterating it. goto statement goto statement transfers the control to the labeled statement. Infinite Loop An infinite loop is executed when the test expression never becomes false and the body of the loop is executed repeatedly. A program is stuck in an Infinite loop when the condition is always true. Mostly this is an error that can be resolved by using Loop Control statements. Using for loop: C // C program to demonstrate infinite // loops using for loop #include // Driver code int main () { int i; // This is an infinite for loop // as the condition expression // is blank for ( ; ; ) { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using While loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { while (1) printf('This loop will run forever.
'); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using the do-while loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using do-while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { do { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } while (1); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ...>