2D pole lze definovat jako pole polí. 2D pole je organizováno jako matice, které mohou být reprezentovány jako kolekce řádků a sloupců.
2D pole jsou však vytvořena pro implementaci relační databáze, která vypadá podobně jako datová struktura. Poskytuje snadné uchovávání velkého množství dat najednou, které lze předat libovolnému počtu funkcí, kdykoli je to potřeba.
Jak deklarovat 2D Array
Syntaxe deklarování dvourozměrného pole je velmi podobná syntaxi jednorozměrného pole, jak je uvedeno níže.
int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
nicméně vytváří datovou strukturu, která vypadá následovně.
C
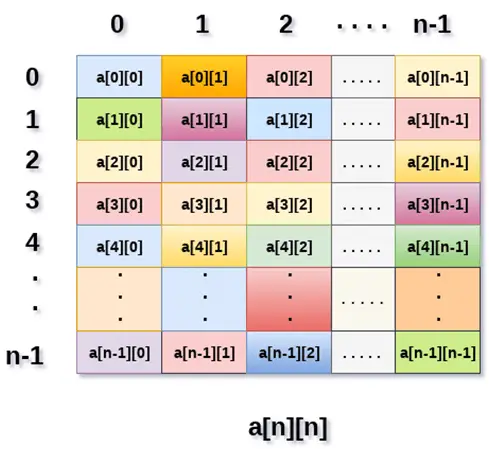
Výše uvedený obrázek ukazuje dvourozměrné pole, prvky jsou uspořádány ve formě řádků a sloupců. První prvek prvního řádku je reprezentován a[0][0], kde číslo zobrazené v prvním indexu je číslo tohoto řádku, zatímco číslo zobrazené ve druhém indexu je číslo sloupce.
Jak přistupujeme k datům ve 2D poli
Vzhledem k tomu, že k prvkům 2D polí lze přistupovat náhodně. Podobně jako u jednorozměrných polí můžeme přistupovat k jednotlivým buňkám ve 2D poli pomocí indexů buněk. Ke konkrétní buňce jsou připojeny dva indexy, jeden je číslo řádku a druhý číslo sloupce.
Hodnotu uloženou v jakékoli konkrétní buňce 2D pole však můžeme uložit do nějaké proměnné x pomocí následující syntaxe.
int x = a[i][j];
kde i a j je číslo řádku a sloupce buňky.
Každou buňku 2D pole můžeme přiřadit 0 pomocí následujícího kódu:
for ( int i=0; i<n ;i++) { for (int j="0;" j<n; j++) a[i][j]="0;" } < pre> <h2>Initializing 2D Arrays </h2> <p>We know that, when we declare and initialize one dimensional array in C programming simultaneously, we don't need to specify the size of the array. However this will not work with 2D arrays. We will have to define at least the second dimension of the array. </p> <p>The syntax to declare and initialize the 2D array is given as follows. </p> <pre> int arr[2][2] = {0,1,2,3}; </pre> <p>The number of elements that can be present in a 2D array will always be equal to ( <strong>number of rows * number of columns</strong> ). </p> <p> <strong>Example :</strong> Storing User's data into a 2D array and printing it. </p> <p> <strong>C Example : </strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf('enter a[%d][%d]: ',i,j); scanf('%d',&arr[i][j]); } printf('
printing the elements ....
'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf('
'); printf('%d ',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print('enter element'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println('printing elements...'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+' '); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline('enter element'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline('printing elements...'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+' '); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></n> Počet prvků, které mohou být přítomny ve 2D poli, bude vždy roven ( počet řádků * počet sloupců ).
strojové učení a typy
Příklad: Ukládání uživatelských dat do 2D pole a jejich tisk.
C Příklad:
#include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf(\'enter a[%d][%d]: \',i,j); scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i][j]); } printf(\'
printing the elements ....
\'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf(\'
\'); printf(\'%d \',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print(\'enter element\'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println(\'printing elements...\'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+\' \'); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline(\'enter element\'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline(\'printing elements...\'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+\' \'); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)> kde B. A. je základní adresa nebo adresa prvního prvku pole a[0][0] .
Příklad:
a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer
Podle hlavního pořadí sloupců
Pokud je pole deklarováno pomocí a[m][n], kde m je počet řádků, zatímco n je počet sloupců, pak se adresa prvku a[i][j] pole uloženého v hlavním pořadí vypočítá jako ,
Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA
kde BA je základní adresa pole.
Příklad:
A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes
