Level Order Traversal Technika je definována jako metoda procházení Stromu tak, že všechny uzly na stejné úrovni jsou zcela procházeny před procházením další úrovně.
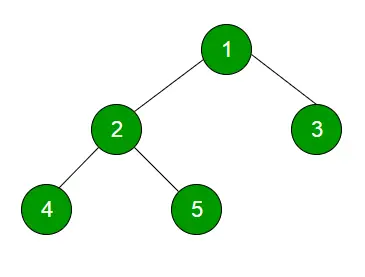
Příklad:
Doporučený postup Procházení objednávky úrovně Vyzkoušejte to!Vstup:
Výstup:
1
23
Čtyři pět
Jak funguje Level Order Traversal?
Hlavní myšlenkou procházení pořadí úrovní je procházet všemi uzly nižší úrovně před přechodem k některému z uzlů vyšší úrovně. To lze provést některým z následujících způsobů:
- ten naivní (zjištění výšky stromu a procházení každé úrovně a tisk uzlů této úrovně)
- efektivně využívat frontu.
Level Order Traversal (Naivní přístup):
Nalézt výška stromu. Poté pro každou úroveň spusťte rekurzivní funkci zachováním aktuální výšky. Kdykoli se úroveň uzlu shoduje, vytiskněte tento uzel.
Níže je uvedena implementace výše uvedeného přístupu:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->data<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Vypočítejte 'výšku' stromu -- počet // uzlů podél nejdelší cesty od kořenového uzlu // dolů k nejvzdálenějšímu listovému uzlu. int vyska(uzel* uzel) { if (uzel == NULL) return 0; else { // Vypočítejte výšku každého podstromu int lheight = height(node->left); int rheight = výška(uzel->vpravo); // Použijte větší if (výška> pravá) { return (výška + 1); } else { return (height + 1); } } } // Pomocná funkce, která alokuje // nový uzel s danými daty a // levým a pravým ukazatelem NULL. node* newNode(int data) { node* Node = new node(); Uzel->data = data; Uzel->left = NULL; Uzel->vpravo = NULL; návrat (Node); } // Kód ovladače int main() { uzel* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->data); else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Vypočítejte 'height' stromu -- počet // uzlů podél nejdelší cesty od kořenového uzlu // dolů k nejvzdálenějšímu listovému uzlu int height(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; else { // Vypočítejte výšku každého podstromu int lheight = height(node->left); int rheight = výška(uzel->vpravo); // Použijte větší if (výška> pravá) return (výška + 1); else return (height + 1); } } // Pomocná funkce, která alokuje nový uzel s // danými daty a levým a pravým ukazatelem NULL. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); uzel->data = data; uzel->left = NULL; uzel->vpravo = NULL; návrat (uzel); } // Program ovladače pro testování výše uvedených funkcí int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); printf('Pořadí úrovně procházení binárního stromu je
'); printLevelOrder(kořen); návrat 0; }> Jáva // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) return (výška + 1); else return (height + 1); } } // Tisk uzlů na aktuální úrovni void printCurrentLevel(kořen uzlu, int úroveň) { if (root == null) return; if (úroveň == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Ovladač pro testování výše uvedených funkcí public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); System.out.println('Procházení pořadí úrovní' + 'binární strom je '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } }> Krajta # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # Vypočítejte výšku stromu – počet uzlů # podél nejdelší cesty od kořenového uzlu dolů k # nejvzdálenějšímu listu node def height(node): if node is None: return 0 else: # Vypočítejte výšku každého podstromu lheight = height(node.left) rheight = height(node.right) # Použijte větší, pokud lheight> rheight: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Program ovladače pro otestování výše uvedené funkce, pokud __name__ == '__main__': root = Uzel(1) root.left = Uzel(2) root.right = Uzel(3) root. left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Procházení pořadím úrovně binárního stromu je -') printLevelOrder(root) # Tento kód přispěl Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) { return (výška + 1); } else { return (height + 1); } } } // Tisk uzlů na aktuální úrovni public virtual void printCurrentLevel(kořen uzlu, úroveň int) { if (kořen == null) { return; } if (úroveň == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Kód ovladače public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); Console.WriteLine('Pořadí úrovní ' + 'binárního stromu je '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } } // Tento kód přispěl Shrikant13> Javascript // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) return (výška + 1); else return (height + 1); } } // Tisk uzlů na aktuální úrovni funkce printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (úroveň == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Program ovladače k testování výše uvedených funkcí root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); console.log('Pořadí úrovně procházení binárního stromu je '); printLevelOrder(); // Tento kód přispěl umadevi9616> Výstup
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Časová náročnost: O(N), kde N je počet uzlů ve zkoseném stromu.
Pomocný prostor: O(1) Pokud se uvažuje zásobník rekurze, použitý prostor je O(N).
dlouhý formát řetězce java
Level Order Traversal pomocí Fronta
Potřebujeme navštívit uzly na nižší úrovni dříve než jakýkoli uzel na vyšší úrovni, tato myšlenka je docela podobná jako u fronty. Posuňte uzly nižší úrovně ve frontě. Když je navštíven jakýkoli uzel, vyjměte tento uzel z fronty a vložte podřízený uzel tohoto uzlu do fronty.
Tím je zajištěno, že uzel nižší úrovně bude navštíven dříve než jakýkoli uzel vyšší úrovně.
Níže je uvedena implementace výše uvedeného přístupu:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Zařadit kořen do fronty a inicializovat výšku q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Tisk přední části fronty a její odstranění z fronty Uzel* node = q.front(); cout<< node->data<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->vlevo != NULL) q.push(uzel->left); // Zařadit pravého potomka if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // Funkce nástroje pro vytvoření nového uzlu stromu Uzel* newNode(int data) { Uzel* temp = new Node; temp->data = data; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; návratová teplota; } // Ovladač pro testování výše uvedených funkcí int main() { // Vytvořme binární strom zobrazený v diagramu výše Uzel* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->data); // Zařadit do fronty levého potomka if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Zařadit do fronty pravého potomka if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Dequeue uzel a udělá z něj temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Užitkové funkce struct node** createQueue(int* přední, int* zadní) { struct node** fronta = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *přední = *zadní = 0; návratová fronta; } void enQueue(struct uzel** fronta, int* zadní, struct uzel* nový_uzel) { fronta[*zadní] = nový_uzel; (*zadní)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct node** fronta, int* front) { (*front)++; návratová fronta[*přední - 1]; } // Pomocná funkce, která alokuje nový uzel s // danými daty a levým a pravým ukazatelem NULL. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); uzel->data = data; uzel->left = NULL; uzel->vpravo = NULL; návrat (uzel); } // Program ovladače pro testování výše uvedených funkcí int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); printf('Pořadí úrovní binárního stromu je
'); printLevelOrder(kořen); návrat 0; }> Jáva // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuefronta = nový LinkedList(); fronta.add(kořen); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() odstraní současnou hlavičku. Node tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Zařadit levého potomka if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // Zařadit do fronty pravého potomka if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Vytvoření binárního stromu a zadání // uzlů BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = new Node(1); tree_level.root.left = new Node(2); tree_level.root.right = new Node(3); tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5); System.out.println('Pořadí úrovně procházení binárního stromu je - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> Krajta # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Vytisknout přední část fronty a # odstranit ji z fronty print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # Zařadit do fronty levé potomky, pokud node.left není Žádný: queue.append(node.left) # Zařadit do fronty pravého potomka, pokud node.right není Žádný: queue.append(node.right) # Program ovladače k otestování výše uvedené funkce, pokud __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Pořadí úrovně Procházení binárního stromu je - ') printLevelOrder(root) # Tento kód přidal Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuefronta = nová fronta(); fronta.Enqueue(kořen); while (queue.Count != 0) { Node tempNode = queue.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Zařadit levého potomka if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Zařadit do fronty pravého potomka if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Kód ovladače public static void Main() { // Vytvoření binárního stromu a zadání // uzlů BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = new Node(1); tree_level.root.left = new Node(2); tree_level.root.right = new Node(3); tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5); Console.WriteLine('Pořadí úrovní ' + 'binárního stromu je - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // Tento kód přispěl PrinceRaj1992> Javascript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> Výstup
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Časová náročnost: O(N) kde N je počet uzlů v binárním stromu.
Pomocný prostor: O(N) kde N je počet uzlů v binárním stromu.