Vzhledem k a speciální binární strom jehož listové uzly jsou spojeny do tvaru a kruhový dvojitě propojený seznam úkolem je najít výška stromu.
Příklady:
Vstup:

výstup: 2
Vysvětlení: Výška binárního stromu po rozpoznání listových uzlů je 2. Ve výše uvedeném binárním stromu 6 5 a 4 jsou listové uzly a tvoří kruhový dvojitě propojený seznam. Zde bude levý ukazatel listového uzlu fungovat jako předchozí ukazatel kruhového dvojitě propojeného seznamu a jeho pravý ukazatel bude fungovat jako další ukazatel kruhového dvojitě propojeného seznamu.Vstup:
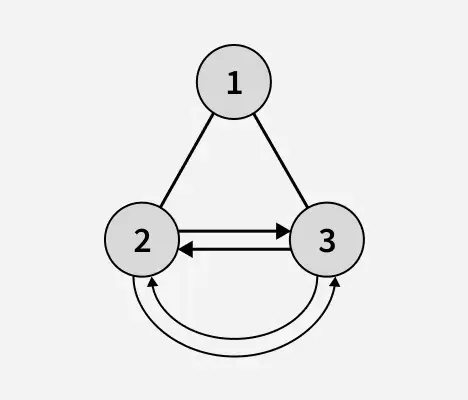
výstup: 1
Vysvětlení: Výška binárního stromu po rozpoznání listových uzlů je 1. Ve výše uvedeném binárním stromu jsou 2 a 3 listové uzly a tvoří kruhový dvojitě propojený seznam.f filmy
Přístup :
C++Smyslem je následovat podobný přístup jako my pro zjištění výšky normálního binárního stromu . My rekurzivně vypočítat výška z vlevo a vpravo podstromy uzlu a přiřadit výška do uzlu jako max z výšek dvou dětí plus 1. Ale levé a pravé dítě a listový uzel jsou null pro normální binární stromy. Ale zde listový uzel je kruhový dvojitě propojený uzel seznamu. Aby byl uzel listovým uzlem, zkontrolujeme, zda uzel zleva doprava ukazuje na uzel a jeho pravá je levá také ukazuje na uzel sám.
// C++ program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// C program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// Java program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static boolean isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; System.out.println(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
# Python program to calculate height of a special tree # whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # function to check if given # node is a leaf node or node def isLeaf(node): # For a node to be a leaf node it should # satisfy the following two conditions: # 1. Node's left's right pointer should be # current node. # 2. Node's right's left pointer should be # current node. # If one condition is met it is guaranteed # that the other condition is also true. return (node.left and node.left.right == node and node.right and node.right.left == node) # Compute the height of a tree def findTreeHeight(node): # if node is NULL return -1. if node is None: return -1 # if node is a leaf node return 0 if isLeaf(node): return 0 # compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)) if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.left.left.left = Node(6) # Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes l1 = root.left.left.left l2 = root.left.right l3 = root.right # create circular doubly linked list out of # leaf nodes of the tree # set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2 l2.right = l3 l3.right = l1 # set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2 l2.left = l1 l1.left = l3 print(findTreeHeight(root))
// C# program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static bool isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.Max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } static void Main(string[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; Console.WriteLine(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
// JavaScript program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node function isLeaf(node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left && node.left.right === node && node.right && node.right.left === node; } // Compute the height of a tree function findTreeHeight(node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node === null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes const l1 = root.left.left.left; const l2 = root.left.right; const l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; console.log(findTreeHeight(root));
Výstup
3
Časová náročnost: O(n) kde n je počet uzlů.
Pomocný prostor: Ó)


