Eulerova funkce Totient Φ(n) pro vstup n je počet čísel v {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}, která jsou relativně prvočíslá k n, tj. čísla, jejichž GCD (největší společný dělitel) s n je 1.
Příklady:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) je 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) je 1, ale gcd(2, 2) je 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) je 1 a gcd(2, 3) je 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) je 1 a gcd(3, 4) je 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) je 1, gcd(2, 5) je 1,
gcd(3, 5) je 1 a gcd(4, 5) je 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) je 1 a gcd(5, 6) je 1,
Doporučený postup Funkce Euler Totient Vyzkoušejte!
Jak vypočítat Φ(n) pro vstup n?
A jednoduché řešení je iterovat všechna čísla od 1 do n-1 a počítat čísla s gcd s n jako 1. Níže je implementace jednoduché metody pro výpočet Eulerovy funkce Totient pro vstupní celé číslo n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Jáva // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Výstup
phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
Výše uvedený kód volá funkci gcd O(n) krát. Časová složitost funkce gcd je O(h), kde h je počet číslic v menším počtu daných dvou čísel. Proto horní mez na časovou složitost výše uvedeného řešení je O(N^2 log N) [Jak Φ může být nejvýše Log10n číslic ve všech číslech od 1 do n]
Pomocný prostor: O(log N)
Níže je a Lepší řešení . Myšlenka je založena na Eulerově součinovém vzorci, který říká, že hodnota totientních funkcí je pod celkovými prvočísly součinu p z n.
Vzorec v podstatě říká, že hodnota Φ(n) se rovná n vynásobenému vedlejším součinem (1 – 1/p) pro všechny prvočinitele p z n. Například hodnota Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Všechny hlavní faktory můžeme najít pomocí myšlenky použité v tento pošta.
výběr řazení
1) Inicializovat: výsledek = n
2) Spusťte smyčku od 'p' = 2 do sqrt(n), pro každé 'p' proveďte následující.
a) Jestliže p dělí n, pak
Sada: výsledek = výsledek * (1,0 - (1,0 / (plovoucí) p));
Vydělte všechny výskyty p v n.
3) Vraťte výsledek
Níže je uvedena implementace vzorce produktu Euler.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; //Protože v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n //pokud n je prvočíslo return (int)result; } // Kód ovladače int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; //Protože v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n //pokud n je prvočíslo return (int)result; } // Program ovladače k otestování výše uvedené funkce int main() { int n; pro (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Jáva // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; //Protože v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n //pokud n je prvočíslo return (int)result; } // Program ovladače k otestování výše uvedené funkce public static void main(String args[]) { int n; pro (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : výsledek -= výsledek // n #Vzhledem k tomu, že v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n #pokud n je prvočíslo return int(result) # Driver program pro otestování výše uvedené funkce pro n v rozsahu (1, 11) : print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Tento kód je autorem # od Nikity Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; //Protože v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n //pokud n je prvočíslo return (int)result; } // Kód ovladače public static void Main() { int n; pro (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; //Protože v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n //pokud n je prvočíslo return parseInt(result); } // Kód ovladače pro (nech n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $výsledek -= $výsledek / $n; //Protože v množině {1,2,...,n-1} jsou všechna čísla relativně prvočísla s n //pokud n je prvočíslo return intval($result); } // Kód ovladače pro ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Výstup
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Časová náročnost: O(Φ n log n)
Pomocný prostor: O(1)
Ve výše uvedené metodě se můžeme vyhnout výpočtům s plovoucí desetinnou čárkou. Cílem je spočítat všechny prvočinitele a jejich násobky a tento počet odečíst od n, abychom získali hodnotu funkce totient (prvočinitele a násobky prvočinitelů nebudou mít gcd jako 1)
java nahradit vše
1) Inicializujte výsledek jako n
2) Uvažujme každé číslo 'p' (kde 'p' se mění od 2 do Φ(n)).
Pokud p dělí n, proveďte následující
a) Odečtěte všechny násobky p od 1 do n [všechny násobky p
bude mít gcd více než 1 (alespoň p) s n]
b) Aktualizujte n opakovaným dělením p.
3) Pokud je redukované n větší než 1, odeberte všechny násobky
z n z výsledku.
Níže je uvedena implementace výše uvedeného algoritmu.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; vrátit výsledek; } // Kód ovladače int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; vrátit výsledek; } // Program ovladače k otestování výše uvedené funkce int main() { int n; pro (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Jáva // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; vrátit výsledek; } // Kód ovladače public static void main (String[] args) { int n; pro (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): vysledek -= int(vysledek / n); vrátit výsledek; # Kód ovladače pro n v rozsahu (1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Tento kód přispěl # mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= vysledek / n; vrátit výsledek; } // Kód ovladače static public void Main () { int n; pro (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledek -= parseInt(vysledek / n); vrátit výsledek; } // Kód ovladače pro (nech n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $výsledek -= (int)$výsledek / $n; vrátit $výsledek; } // Kód ovladače pro ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Výstup
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Časová náročnost: O(Φ n log n)
Pomocný prostor: O(1)
Vezměme si příklad pro pochopení výše uvedeného algoritmu.
n = 10.
Inicializace: výsledek = 10
2 je prvočíslo, takže n = n/i = 5, výsledek = 5
3 není primární faktor.
Smyčka for se zastaví po 3, protože 4*4 není menší nebo rovno
do 10.
Po cyklu for je výsledek = 5, n = 5
Protože n> 1, výsledek = výsledek - výsledek/n = 4
Některé zajímavé vlastnosti Eulerovy funkce Totient
1) Pro prvočíslo p ,
důkaz:
Příklady:
int do řetězce java
2) Pro dvě prvočísla a a b
důkaz:
Příklady:
3) Pro prvočíslo p ,
jarní mvc
důkaz:
Příklady:
4) Pro dvě čísla a a b
Zvláštní případ: gcd(a, b) = 1
Příklady:
Speciální případ :
5) Součet hodnot totientních funkcí všech dělitelů n je roven n.
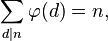
Příklady:
n = 6
faktory = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
mysql zobrazit všechny uživatele
6) Nejznámější a nejdůležitější rys je vyjádřen v Eulerova věta :
Věta říká, že jestliže n a a jsou coprime
(nebo relativně prvočísla) kladná celá čísla, pak
AΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
The kryptosystém RSA je založen na této větě:
V konkrétním případě, kdy je m prvočíslo řekněme p, se Eulerova věta změní v tzv Fermatova malá věta :
Ap-1Φ 1 (proti p)
7) Počet generátorů konečné cyklické grupy při sčítání modulo n je Φ(n) .
Související článek:
Eulerova funkce Totient pro všechna čísla menší nebo rovna n
Optimalizovaná funkce Euler Totient pro vícenásobná hodnocení
Reference:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
