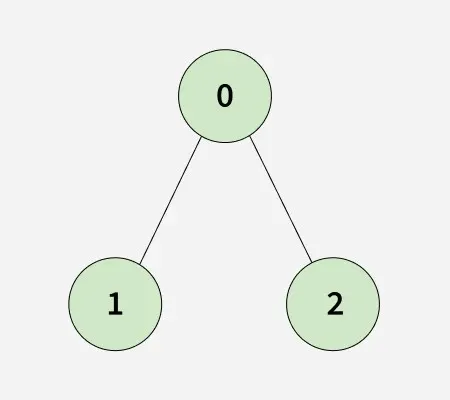
Vzhledem k a připojený neorientovaný graf reprezentovaný seznamem sousedství adjList[][] s n uzly a m hrany, přičemž každý uzel má a zřetelný štítek z 0 až n-1 a každé adj[i] představuje seznam vrcholů připojených k vertexu i.
Vytvořte a klon grafu, kde každý uzel v grafu obsahuje celé číslo val a pole ( sousedé ) uzlů obsahující uzly, které sousedí s aktuálním uzlem.
class Node {
val: celé číslo
sousedé: Seznam[Uzel]
}
Vaším úkolem je naklonovat daný graf a vrátit odkaz na naklonovaný graf.
Poznámka: Pokud vrátíte správnou kopii daného grafu, výstup bude pravdivý; jinak pokud je kopie nesprávná, vytiskne se falešně.
jak stahovat videa z youtube vlc
Příklady
Vstup: n = 4 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0 2] [0 1 3] [2]]
výstup: věrný
Vysvětlení:
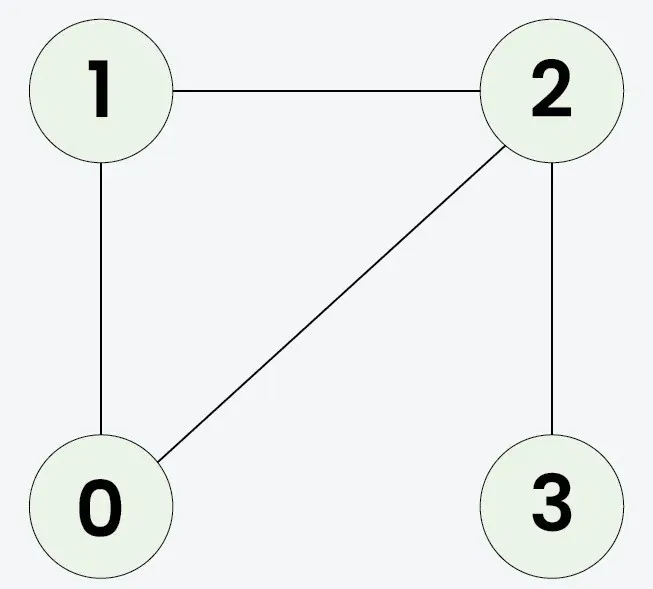
Protože je klonovaný graf identický s originálem, výstup bude pravdivý.Vstup: n = 3 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0] [0]]
výstup: věrný
Vysvětlení:
Protože je klonovaný graf identický s originálem, výstup bude pravdivý.
Obsah
- Proč potřebujeme sledovat navštívené/klonované uzly?
- Jak sledovat navštívené/klonované uzly?
- Jak připojit klonované uzly?
- Jak ověřit, zda je klonovaný graf správný?
- [Přístup 1] Použití BFS traversal – O(V+E) čas a O(V) prostor
- [Přístup 2] Použití DFS traversal – O(V+E) čas a O(V) prostor
Proč potřebujeme sledovat navštívené/klonované uzly?
Potřebujeme sledovat navštívené nebo klonované uzly, abychom se vyhnuli nekonečné rekurzi a nadbytečné práci při klonování grafu. Vzhledem k tomu, že grafy mohou obsahovat cykly (kde může uzel ukazovat zpět na dříve navštívený uzel), bez sledování uzlů, které jsme již naklonovali, by funkce klonování donekonečna znovu navštěvovala stejné uzly, což by vedlo k přetečení zásobníku nebo nesprávné duplikaci.
Jak sledovat navštívené/klonované uzly?
HashMap/Map je vyžadována pro zachování všech uzlů, které již byly vytvořeny. Klíčové sklady : Reference/Adresa původního uzlu Hodnotové obchody : Reference/Adresa klonovaného uzlu Byla vytvořena kopie všech uzlů grafu.
Jak připojit klonované uzly?
Při návštěvě sousedních vrcholů a uzel v získat odpovídající klonování uzel pro tebe to nazvěme V nyní navštivte všechny sousední uzly v a pro každého souseda najděte odpovídající klonový uzel (pokud nebyl nalezen, vytvořte jej) a poté jej vložte do sousedního vektoru V uzel.
Jak ověřit, zda je klonovaný graf správný?
Proveďte BFS traversal na původním grafu před klonováním a poté znovu na klonovaném grafu po dokončení klonování. Během každého průchodu se vytiskne hodnota každého uzlu spolu s jeho adresou (nebo odkazem). Pro ověření správnosti klonování porovnejte pořadí uzlů navštívených v obou průchodech. Pokud se hodnoty uzlů objeví ve stejném pořadí, ale jejich adresy (nebo reference) se liší, potvrzuje to, že graf byl úspěšně a správně naklonován.
prázdný seznam java
Prozkoumejte, jak na to klonovat neorientovaný graf včetně grafů s více připojenými komponentami pomocí BFS nebo DFS k zajištění úplné hluboké kopie všech uzlů a hran.
[Přístup 1] Použití BFS traversal – O(V+E) čas a O(V) prostor
C++V přístupu BFS je graf klonován iterativně pomocí fronty. Začneme klonováním počátečního uzlu a jeho umístěním do fronty. Jak zpracováváme každý uzel z fronty, navštěvujeme jeho sousedy. Pokud soused ještě nebyl naklonován, vytvoříme klon, uložíme jej do mapy a zařadíme do fronty pro pozdější zpracování. Potom přidáme klon souseda do seznamu sousedů klonu aktuálního uzlu. Tento proces pokračuje úroveň po úrovni a zajišťuje, že všechny uzly jsou navštěvovány v pořadí od šířky jako první. BFS je zvláště užitečné pro zamezení hluboké rekurze a efektivní zpracování velkých nebo širokých grafů.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { public int val; public ArrayList<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Map<Node Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Clone the starting node Node clone = new Node(node.val); mp.put(node clone); q.offer(node); while (!q.isEmpty()) { Node current = q.poll(); for (Node neighbor : current.neighbors) { // Clone neighbor if it hasn't been cloned yet if (!mp.containsKey(neighbor)) { mp.put(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.offer(neighbor); } // Add the clone of the neighbor to the current node's clone mp.get(current).neighbors.add(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node2 node3))); node2.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node3))); node3.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node2 node4))); node4.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node3))); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static boolean compareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || n1 == n2) return false; visited.put(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.size() != n2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node neighbor1 = n1.neighbors.get(i); Node neighbor2 = n2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) != neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); boolean isEqual = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
from collections import deque # Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0): self.val = val self.neighbors = [] # Clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): if not node: return None # Map to hold original nodes as keys and their clones as values mp = {} # Initialize BFS queue q = deque([node]) # Clone the starting node mp[node] = Node(node.val) while q: current = q.popleft() for neighbor in current.neighbors: # If neighbor not cloned yet if neighbor not in mp: mp[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val) q.append(neighbor) # Link clone of neighbor to the clone of the current node mp[current].neighbors.append(mp[neighbor]) return mp[node] # Build graph def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs structurally and by values def compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): if not n1 or not n2: return n1 == n2 if n1.val != n2.val or n1 is n2: return False visited[n1] = n2 if len(n1.neighbors) != len(n2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(n1.neighbors)): neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i] neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i] if neighbor1 in visited: if visited[neighbor1] != neighbor2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited): return False return True # Driver if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() cloned = cloneGraph(original) result = compareGraphs(original cloned {}) print('true' if result else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Definition for a Node public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; var mp = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); var q = new Queue<Node>(); // Clone the starting node var clone = new Node(node.val); mp[node] = clone; q.Enqueue(node); while (q.Count > 0) { var current = q.Dequeue(); foreach (var neighbor in current.neighbors) { // If neighbor not cloned clone it and enqueue if (!mp.ContainsKey(neighbor)) { mp[neighbor] = new Node(neighbor.val); q.Enqueue(neighbor); } // Add clone of neighbor to clone of current mp[current].neighbors.Add(mp[neighbor]); } } return mp[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { var node1 = new Node(0); var node2 = new Node(1); var node3 = new Node(2); var node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node2 node3 }); node2.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node3 }); node3.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node2 node4 }); node4.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node3 }); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static bool CompareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || ReferenceEquals(n1 n2)) return false; visited[n1] = n2; if (n1.neighbors.Count != n2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.Count; i++) { var neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; var neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(neighbor1)) { if (!ReferenceEquals(visited[neighbor1] neighbor2)) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void Main() { var original = BuildGraph(); var cloned = CloneGraph(original); var visited = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); Console.WriteLine(CompareGraphs(original cloned visited) ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Clone the graph function cloneGraph(node) { if (!node) return null; const mp = new Map(); const q = [node]; // Clone the initial node mp.set(node new Node(node.val)); while (q.length > 0) { const current = q.shift(); for (const neighbor of current.neighbors) { if (!mp.has(neighbor)) { mp.set(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.push(neighbor); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current mp.get(current).neighbors.push(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors = [node2 node3]; node2.neighbors = [node1 node3]; node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4]; node4.neighbors = [node3]; return node1; } // Compare two graphs structurally and by value function compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited = new Map()) { if (!n1 || !n2) return n1 === n2; if (n1.val !== n2.val || n1 === n2) return false; visited.set(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.length !== n2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.length; i++) { const neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; const neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) !== neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver const original = buildGraph(); const cloned = cloneGraph(original); const result = compareGraphs(original cloned); console.log(result ? 'true' : 'false');
Výstup
true
[Přístup 2] Použití DFS traversal – O(V+E) čas a O(V) prostor
C++V přístupu DFS je graf klonován pomocí rekurze. Začneme od daného uzlu a před návratem prozkoumáme co nejdále podél každé větve. Mapa (nebo slovník) se používá ke sledování již klonovaných uzlů, aby se předešlo opakovanému zpracování stejného uzlu a zpracování cyklů. Když se s uzlem setkáme poprvé, vytvoříme jeho klon a uložíme jej do mapy. Poté pro každého souseda tohoto uzlu rekurzivně naklonujeme a přidáme klonovaného souseda do klonu aktuálního uzlu. To zajišťuje, že všechny uzly jsou před návratem hluboce navštíveny a struktura grafu je věrně zkopírována.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { int val; ArrayList<Node> neighbors; Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Map to hold original node to its copy static HashMap<Node Node> copies = new HashMap<>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.containsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies.put(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node2 node3)); node2.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1 node3)); node3.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1node2 node4)); node4.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node3)); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static boolean compareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited.put(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.size() != node2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors.get(i); Node n2 = node2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) != n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph boolean result = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(result ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
# Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0 neighbors=None): self.val = val self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else [] # Map to hold original node to its copy copies = {} # Function to clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): # If the node is None return None if not node: return None # If node is not yet cloned clone it if node not in copies: # Create a clone of the node clone = Node(node.val) copies[node] = clone # Recursively clone neighbors for neighbor in node.neighbors: clone.neighbors.append(cloneGraph(neighbor)) # Return the clone return copies[node] def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs for structural and value equality def compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited): if not node1 or not node2: return node1 == node2 if node1.val != node2.val or node1 is node2: return False visited[node1] = node2 if len(node1.neighbors) != len(node2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(node1.neighbors)): n1 = node1.neighbors[i] n2 = node2.neighbors[i] if n1 in visited: if visited[n1] != n2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() # Clone the graph using DFS cloned = cloneGraph(original) # Compare original and cloned graph visited = {} print('true' if compareGraphs(original cloned visited) else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Dictionary to hold original node to its copy static Dictionary<Node Node> copies = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.ContainsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies[node] = clone; // Recursively clone neighbors foreach (Node neighbor in node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.Add(CloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.Add(node2); node1.neighbors.Add(node3); node2.neighbors.Add(node1); node2.neighbors.Add(node3); node3.neighbors.Add(node1); node3.neighbors.Add(node2); node3.neighbors.Add(node4); node4.neighbors.Add(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static bool CompareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited[node1] = node2; if (node1.neighbors.Count != node2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.Count; i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; Node n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(n1)) { if (visited[n1] != n2) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { Node original = BuildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS Node cloned = CloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph bool isEqual = CompareGraphs(original cloned new Dictionary<Node Node>()); Console.WriteLine(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Map to hold original node to its copy const copies = new Map(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS function cloneGraph(node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node === null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.has(node)) { const clone = new Node(node.val); copies.set(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (let neighbor of node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.push(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.push(node2 node3); node2.neighbors.push(node1 node3); node3.neighbors.push(node1 node2 node4); node4.neighbors.push(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality function compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited = new Map()) { if (!node1 || !node2) return node1 === node2; if (node1.val !== node2.val || node1 === node2) return false; visited.set(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.length !== node2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.length; i++) { const n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; const n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) !== n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code const original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS const cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph console.log(compareGraphs(original cloned) ? 'true' : 'false');
Výstup
true