Vzhledem k a dvojitě propojený seznam z postavy úkolem je zkontrolovat, zda je dvojitě propojený seznam a palindrom nebo ne.
Příklady:
Vstup:
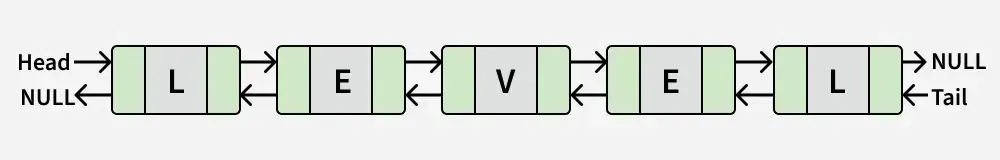
výstup: Věrný
Vysvětlení: Seznam odpovídá 'LEVEL', což je palindrom.Java vylepšená smyčka
Vstup:
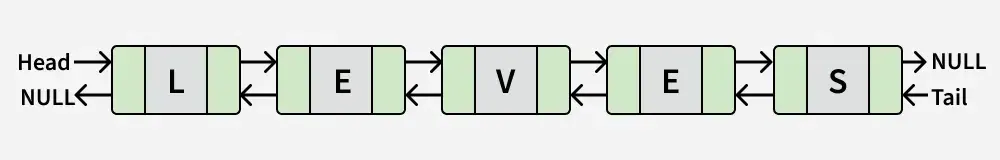
výstup: Falešný
Vysvětlení: Seznam odpovídá 'LEVES', což není palindrom.
Přístup:
Cílem je inicializovat dva ukazatele: vlevo (zpočátku nastaveno na hlavu) a právo (zpočátku nastaveno na ocas). Porovnejte hodnoty dvou ukazatelů while vlevo se nerovná nule nebo vlevo se přesunul na další z právo. Pokud jsou hodnoty dvou ukazatelů rovný pohyb vlevo na další ukazatel a právo na předchozí ukazatel. Jinak vrátí false.
třídicí řetězce java
Níže je uvedena implementace výše uvedeného přístupu:
C++// C++ program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. #include
// C program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. #include
// Java program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. class Node { char data; Node prev next; Node(char x) { data = x; prev = null; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome static boolean isPalindrome(Node head) { if (head == null) return true; // Find the tail ptr. Node left = head right = head; while (right.next != null) { right = right.next; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while (left != right && left.prev != right) { // If char mismatch return // false. if (left.data != right.data) return false; // Move the pointers left = left.next; right = right.prev; } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node head = new Node('L'); head.next = new Node('E'); head.next.prev = head; head.next.next = new Node('V'); head.next.next.prev = head.next; head.next.next.next = new Node('E'); head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next = new Node('L'); head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next; if (isPalindrome(head)) System.out.println('True'); else System.out.println('False'); } }
# Python program to check if a doubly # linked list is palindrome. class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.prev = None self.next = None # Function that returns true if the # doubly linked list is a palindrome def isPalindrome(head): if head is None: return True # Find the tail ptr. left = head right = head while right.next is not None: right = right.next # Check if the doubly linked list is # a palindrome. while left != right and left.prev != right: # If char mismatch return # false. if left.data != right.data: return False # Move the pointers left = left.next right = right.prev return True if __name__ == '__main__': # Doubly Linked list: # L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L head = Node('L') head.next = Node('E') head.next.prev = head head.next.next = Node('V') head.next.next.prev = head.next head.next.next.next = Node('E') head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next = Node('L') head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next if isPalindrome(head): print('True') else: print('False')
// C# program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. using System; class Node { public char data; public Node prev next; public Node(char x) { data = x; prev = null; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome static bool isPalindrome(Node head) { if (head == null) return true; // Find the tail ptr. Node left = head right = head; while (right.next != null) { right = right.next; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while (left != right && left.prev != right) { // If char mismatch return // false. if (left.data != right.data) return false; // Move the pointers left = left.next; right = right.prev; } return true; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node head = new Node('L'); head.next = new Node('E'); head.next.prev = head; head.next.next = new Node('V'); head.next.next.prev = head.next; head.next.next.next = new Node('E'); head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next = new Node('L'); head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next; if (isPalindrome(head)) Console.WriteLine('True'); else Console.WriteLine('False'); } }
// JavaScript program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.prev = null; this.next = null; } } // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome function isPalindrome(head) { if (head === null) return true; // Find the tail ptr. let left = head right = head; while (right.next !== null) { right = right.next; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while (left !== right && left.prev !== right) { // If char mismatch return // false. if (left.data !== right.data) return false; // Move the pointers left = left.next; right = right.prev; } return true; } // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L let head = new Node('L'); head.next = new Node('E'); head.next.prev = head; head.next.next = new Node('V'); head.next.next.prev = head.next; head.next.next.next = new Node('E'); head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next = new Node('L'); head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next; if (isPalindrome(head)) console.log('True'); else console.log('False');
Výstup
True
Časová složitost: O(n) kde n je počet uzlů ve dvojitě propojeném seznamu.
Pomocný prostor: O(1)
Související články:
- Funkce pro kontrolu, zda je jednotlivě propojený seznam palindrom
- Zkontrolujte, zda propojený seznam řetězců tvoří palindrom


